Case Study of Plant Metabolomics: Response of Soybean Seedling Leaves to Salt Stress
Genomics : Response of Soybean Seedling Leaves to Salt Stress
Subject: Soy
Analytical detection platform: GC-TOF/MS (BIOTREE)
Journal: PLoS ONE
Impact factor: 3.057
Published time: 2016
Summary:
Clarification of the metabolic mechanisms underlying salt stress responses in plants will allow further optimization of crop breeding and cultivation to obtain high yields in salinealkali land. Here, we characterized 68 differential metabolites of cultivated soybean (Glycine max) and wild soybean (Glycine soja) under Neutral-salt and alkali-salt stresses using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomics, to reveal the physiological
And molecular differences in salt tolerance. According to comparisons of growth parameters under the two kinds of salt stresses, the level of inhibition in wild soybean was lower than in cultivated soybean, especially under alkali-salt stress. Of phenylalanine, asparagine, citraconic acid, citramalic acid, citric acid and α-ketoglutaric acid under neutral-salt stress, and higher amounts of palmitic acid, lignoceric acid, glucose, citric acid and α-ketoglutaric acid under alkali-salt stress, than Developed soybean. Further investigations demonstrated that the ability of wild soybean to salt tolerance was primarily based on the synthesis of organic and amino acids, and the more active tricarboxylic acid cycle under neutral-salt stress. In addition, the metabolite profiling analysis suggested that the Energy generation from β-oxidation, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle plays important roles under alkali-salt stress. Sults extend the understanding of mechanisms involved in wild soybean salt tolerance and provide an important reference for increasing yields and developing salt-tolerant soybean cultivars.
First, the research background:
Soybean is an important economic and oil crop. However, its salt tolerance is gradually reduced during the cultivation process, which seriously affects plant growth and product quality. Wild soybeans are closely related to cultivated soybeans, but often exhibit stronger salt tolerance. Through the study of wild plants, the expression of Na+, antioxidant enzymes and secondary metabolic pathways in different parts of the plant have an effect on the salt tolerance process. During the stress process, the wild plants have higher accumulation of amino acids and disaccharides, and the unsaturated fatty acids, carboxylic acids and monosaccharides are lower than the cultivated plants. Metabolomics can more fully reveal the response process of plants to the environment, including plant functions, metabolic networks, metabolic regulation mechanisms and phenotypes, all of which can be studied by examining metabolites. Previous metabolomics research tools have been widely used in the analysis of plant stress processes. In this paper, we try to find out the metabolic pathways related to salt tolerance of soybeans from the plants with different tolerances and provide the basis for subsequent metabolic engineering.
Second, the method flow:
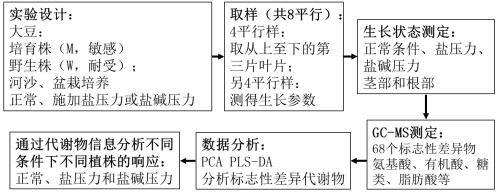
Third, the research results and discussion:
1 difference in growth status :
1) W (wild strain) is significantly better than M (cultivated strain) under salt pressure or saline-alkali pressure.
2) Saline-alkali pressure causes more serious growth decline than neutral salt pressure

Figure 1 Growth performance of different plants under saline-alkali pressure
2 Analysis of metabolite differences in soybean under different conditions
1) Principal component analysis (PCA) indicates an overall change in the metabolites of plants under different conditions;
2) Normal conditions: TCA cycle and productivity pathway are active in W, and amino acid synthesis in M ​​is active;
3) Salt pressure: TCA cycle in W, organic acid and amino acid synthesis strengthen
4) Saline-alkali pressure: Stearic acid, citric acid, and wood wax acid accumulate in W, and decrease in M; G-glycolysis and TCA cycle are strengthened in W, and M is weakened.
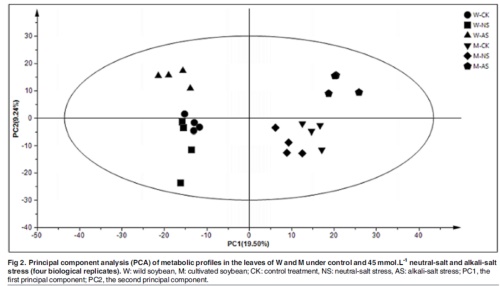
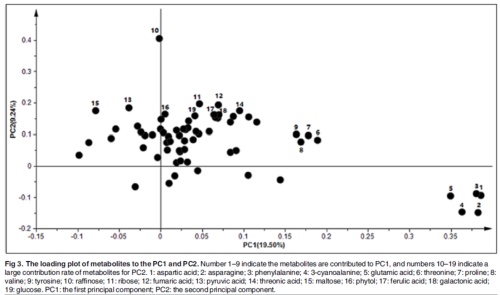
Fig. 2 Statistical analysis of multivariate variables Establishing score map and sample plot of PCA A model
3 Tolerance mechanism of wild soybean under saline-alkali pressure
1) reducing the intracellular water potential by accumulating small molecular metabolites such as organic acids and amino acids;
2) activate the antioxidant pathway through signal molecules such as salicylic acid (SA) and squalene to reduce the degree of lipid peroxidation in the cell membrane;
3) Salt pressure: TCA cycle, enhanced synthesis of organic acids, amino acids and fatty acids in W
Fourth, highlights and prospects:
By setting different intensity salt pressure conditions, we investigated the progressive increasing stress strategy of wild soybean (W tolerant strain).
A key response pathway is obtained by excluding metabolic changes that are not associated with tolerance, as compared to cultivating soybeans (M-sensitive strains);
The stress strategy of wild soybean was proposed by metabolomics analysis: improving the compatibility of solute accumulation and productivity pathway;
Prospect: The established tolerance-related pathways can be combined with transcriptomics and proteomics to identify key stress response pathways;
Outlook: Metabolomics has discovered a relatively macroscopic mechanism of salinity tolerance, and more specific metabolic engineering targets have to be obtained through investigation of key genes.
Read the literature download address:
Zhang J, Yang D, Li M, et al. Metabolic Profiles Reveal Changes in Wild and Cultivated Soybean Seedling Leaves under Salt Stress: [J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(7).
Baby Wet Wipes are disposable wipes that are specifically designed for cleaning the delicate skin of babies. They are made from soft, gentle, and non-irritating materials that are safe for use on babies' skin. Baby wet wipes are pre-moistened with a mild cleansing solution that helps to clean and moisturize the skin while removing dirt, grime, and other impurities. They are commonly used for diaper changes, cleaning up after feeding, and for general cleaning of the baby's face and hands. Baby wet wipes are convenient, easy to use, and can be carried in a diaper bag or purse for use on-the-go. They are available in various sizes and scents to suit different preferences and needs.
Baby Wet Wipes,Baby Cleansing Wet Wipes,Flushable Baby Cleaning Wipes,Oem Disposable Baby Wipes
Honghu Danielle Sanitary Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.daniellecn.com