Plant growth regulators introduce what regulator products are currently the most widely used
Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs): Compounds that have been synthesized, biofermented, and extracted have similar physiological activities as endogenous hormones or can affect the synthesis, transportation, metabolism, and physiological activities of endogenous hormones. PGRs do not provide the mineral elements needed for plant growth and development, have no nutritional effects, and are not a substitute for plant nutrients. It only affects the growth and development of plants by regulating the physiological activities of plants, and generally does not participate in the structural composition of plants.
A brief history of the world's PGRs application
The application history of PGRs can be traced back to the 1st century AD. It was known that the dripping of olive oil on the fig tree promoted the development of figs. Later, it was known that high temperature decomposed the olive oil, and the released ethylene affected the development of the fig. In the 1920s, it was discovered that smoking can cause pineapple to bloom. It was not until the 1930s that people understood that the reason why smoke caused pineapple to bloom was that the smoke contained ethylene, which promoted the flowering of pineapple.
The research and application of PGRs actually started in the 1930s and then developed rapidly. In the 1930s, plant physiologists, Thimann and Skoo, conducted research on the apical dominance of indoleacetic acid (IAA) on plant apical dominance, rooting and seedless fruit formation, marking the beginning of research and application of PGRs.
In the 1940s, with the synthesis of new PGRs, especially the synthesis of phenolic compounds, the application range of PGRs was greatly promoted. In addition to promoting rooting, it also includes pre-harvest fruit for fruit trees, promotes fruiting, forms seedless fruits, eliminates body sleep, inhibits germination and chemical weeding. The biggest achievement of this period was the successful screening of 2,4-D.
In the 1950s, in addition to the increasing application range of auxin-based PGRs, the application of gibberellin (GA) has also emerged, and the application range of PGRs has expanded to flowering and fruiting. During this period, people began to use GA to treat crops and succeeded.
In the 1960s and 1970s, ABA (abscisic acid) and ETH (ethylene) were included in the plant-like category. The scope of application of PGRs continues to expand.
In the 1980s, the application of PGRs in production continued to show new breakthroughs. During this period, the market for hyperthyroidism made a great leap in cotton production (China R&D).
So far, the use of PGRs includes promoting germination, rooting, growth, flowering, maturation, inhibiting germination, preventing lodging, breaking the top edge, controlling plant type, maintaining flowers and fruits, thinning flowers and fruit, regulating sex, chemical killing, and improving quality. Enhance resistance, store and keep fresh, promote defoliation, promote dryness, inhibit breathing and inhibit transpiration.
At the end of the 20th century, many new PGRs were discovered, such as brassinolide, polyamine, jasmonic acid, etc., which also had strong physiological activity.
At present, hundreds of PGRs have been artificially synthesized, and dozens of them have been widely used in agricultural production. The regulation of PGRs is an important way to increase production and income of crops at present and in the future.
A brief history of the application of PGRs in China
In our research on the application of plant hormones, plant physicists in China began with the promotion of seedless fruits and the promotion of cutting roots.
In the 1950s, small-scale production demonstrations such as indole acetic acid (IAA), 2,4-D, and naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) were gradually carried out, in which the fruit was prevented from falling before harvest, the cotton was prevented from falling, and the tomato and eggplant were prevented from falling. Has been promoted and applied.
In 1963, China successfully synthesized chlormequat (CCC) and achieved significant results in controlling cotton length and preventing wheat lodging.
In 1971, the successful trial of ethephon was widely used.
In the 1980s, the largest change in the field of cotton cultivation technology in China, the application of a carbamide (decrease), it replaced chlormequat as a cotton plant to delay vegetative growth, shorten internodes, shape ideal plant types, improve lighting conditions, Increase the first growth retardant for ringing.
In recent years, the research, synthesis, and application of PGRs in China have also developed rapidly, and the output has increased year by year. Further research on gibberellin, ethephon, formazan, paclobutrazol, uniconazole, DA-6, etc. has made great progress. Economic and social benefits.
PGRs application status
Plant growth regulators began to be classified as fertilizer management and were classified as pesticide management after the 1990s.
Overall situation:
The world pesticide market is 38.20 billion US dollars (crop protection part), and the planting agent share accounts for 5% (about 3% of China), but it grows at a rate of 10%.
The US EPA has approved more than 20 kinds of PGRs and more than 200 varieties.
International agrochemical giants have stepped into the PGRs business and are constantly acquiring professional companies.
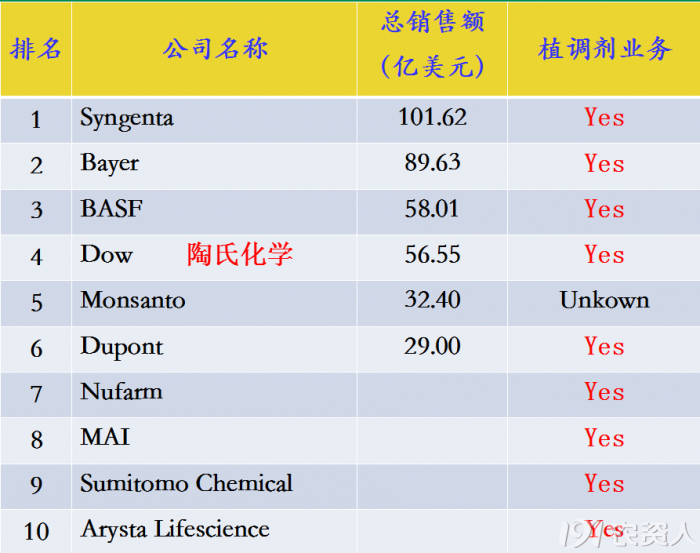
Top 10 global pesticide sales
Syngenta: anti-pourin ester, fluorohexamine
Bayer: cotton defoliant (thiablon, defoliation, ethephon)
BASF: calcium cyclate, dihydrogibberellin
Dow: 1-methylcyclopropene (2008 acquisition of RohmHass)
Nufarm: monocyanamide, etc.
SumitomoChemical: ProGibb®, AVG
ArystaLifescience: sodium nitrophenolate
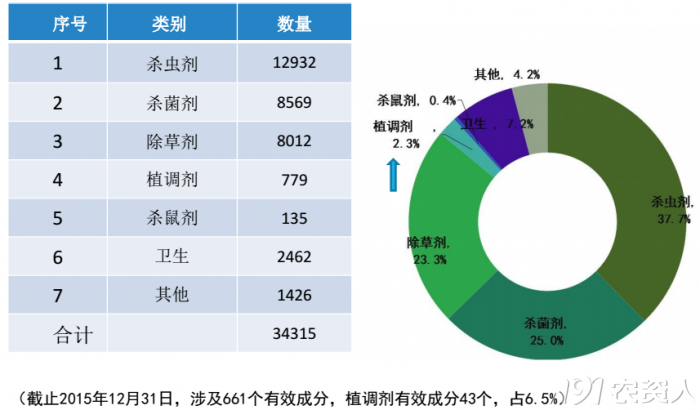
Domestic PGRs registration status
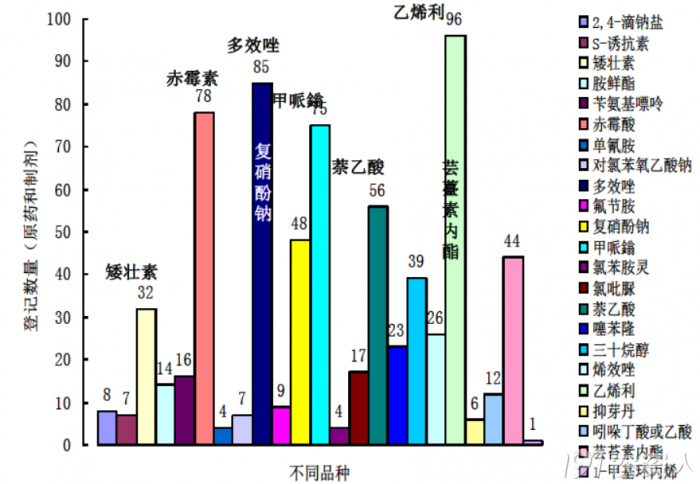
Ethephon, paclobutrazol, gibberellin, and mepivatrid have many registered varieties. Chlorpyrifos and thiabendazole are relatively small.
(Chen Jinyong)
This article URL: Plant Growth Regulators Introduction What regulator products are currently the most widely used
Insect net greenhouse also known as plant and vegetables greenhouse net. Used for prevent the insect fly into the greenhouse during the plant growing, and cover the plants. Key off the approaches that the pests (adult insect) breeding. Effective control of the spread of all kinds of harmful pests spread, such as Cabbage caterpillar, diamondback moth, aphids, flea beetles, Sweet agnates, American leaf miner, literal etc and prevent the harmful of virus spread. Significantly reduced the use of chemical pesticides, so that the planting vegetables good-quality and health.
Greenhouse Insect Net,Insect Mesh Netting,Insect Mesh
JIANGSU SKYPLAN GREENHOUSE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.alibabagreenhouse.com