Cell Technology Topic: Primary Culture of Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes
Primary culture of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes can be: (1) cell preservation; (2) for cell morphology studies; (3) for clinical research.
experimental method
- Trypsin digestion
| Principle of experimental method | The rat cardiomyocytes are taken out from the body, treated with trypsin and a chelating agent (usually EDTA), dispersed into single cells, and cultured in a suitable medium to allow the cells to survive, grow and multiply. |
|---|---|
| Experimental Materials | SD suckling rat |
| Reagents, kits | Low-sugar DMEM, trypsin EDTA, streptomycin, sodium bicarbonate, newborn calf serum, glutamine D-Hank's, liquid, fresh, iodine, alcohol |
| Instruments, consumables | Aluminum box ophthalmology direct cut ophthalmology bending eye ophthalmology straight eye ophthalmology bending glass culture dish jar cotton ball beaker cone bottle centrifuge tube magnetic stirrer stirrer water bath oscillator nylon mesh needle filter |
| Experimental procedure | First, the preparation of experimental materials Animal 15 SD rats were 1-4 days after birth. 2. Reagent Low-sugar DMEM, trypsin (including EDTA), penicillin, sodium bicarbonate, newborn calf serum, glutamine, D-Hank's solution. 0.1% benzalkonium, iodine, 75% alcohol, culture solution (DMEM, newborn bovine serum, penicillin). 3. Surgical instruments and instruments Aluminum box, ophthalmic direct shear, ophthalmic bending, ophthalmology straight, ophthalmic bending, glass culture dish (2 sets, one set for anatomy, another set for cutting heart tissue), 100 ml jar (Iodine and alcohol cotton balls, respectively), 500 ml beaker, 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask, 15 ml and 50 ml centrifuge tubes, magnetic stirrer and stirrer (or water bath shaker), 150-200 mesh nylon screen And needle filter. Second, the method 1. The pancreatin was mixed with D-Hank's solution to a concentration of 0.06%, and placed in a 37 ° C water bath for incubation. 2. Dissection of the material: Put the suckling mouse into 0.1% Xinjieer and soak it, take it with another big scorpion and take the iodine cotton ball to wipe the skin, then use the alcohol cotton ball to remove iodine. The left hand squeezes the skin of the neck of the suckling mouse to fully expose the chest. The right hand takes an ophthalmic direct cut and cuts the skin, fully tears it apart, and then disinfects it with an alcohol cotton ball. Take an ophthalmic bending scissors and cut it along the lower left edge of the sternum stem. Open the ribs and then cut the sternum in the middle of the incision. So as long as the left hand is slightly topped, the heart of the suckling mouse jumps out directly. Then use the ophthalmic curve to cut the ventricle directly from the middle of the heart and place it in the D-Hank's solution in the ice bath. Repeat the above process. After the material is taken, the surgical instruments taken are removed. Note: In order to ensure the vitality of the cardiomyocytes, the operation of the coring is as fast as possible. In addition, it is best to place the culture dish of the heart on the ice table or the pre-cooled balanced salt solution. 3. Use the second set of surgical instruments to perform the following operations. Use the ophthalmology straight and ophthalmic bending scissors to remove the blood clots and fibrous tissue around the heart in the culture dish, put them in another petri dish pre-filled with D-Hank's solution, and wash the heart tissue again. Place the heart tissue in another dish (or other suitable container, depending on your personal habits), add a little 0.06% trypsin, cut the heart tissue into 1mm 3 pieces with ophthalmic bending, and cut the heart and Transfer the trypsin solution into a conical flask with a stirrer. Dip 2-3 ml of fresh trypsin rinse plate and scissors and transfer to a conical flask. Add trypsin to a final volume of 10 ml, add stopper. Place in a 37 ° C water bath (you can use a sterile 500 ml beaker, install sterile distilled water, add enough water, the water line is slightly lower than the 250 ml cone bottle, too little temperature will not Uniform, too high and easy to pollute. Turn on the magnetic stirrer power supply, adjust the water temperature to 37 °C in advance, adjust the rotation speed to about 60 rpm, digest for 15 min (make sure the water bath temperature is constant at 37 ° C, and the digestion time does not exceed 15 min) . Or, if a water bath shaker is used, it can be directly digested in a water bath shaker without adding a stirrer, and the rotation speed and digestion time are the same. 4. Remove the conical flask from the water bath and carefully aspirate the supernatant. The main components in the supernatant are red blood cells and fibroblasts. 5. Add 10 ml of new trypsin, blow the solution several times with a new pipette, and mechanically disperse the cells (the tissue will become a sticky colloid after digestion). Note: Do not over-blow, otherwise it will cause excessive tissue digestion. Stir in the 37 ° C water bath for another 10-15 min; if the number of suckling mice is small (such as 5 or 6), the digestion time can be reduced to 5-10 min, otherwise it is easy to digest. While digesting as above, add 20 ml of pre-cooled medium containing 10% serum to a 50 ml disposable sterile centrifuge tube and place on ice platform. After the digestion treatment, carefully remove the supernatant and transfer to the above-mentioned centrifuge tube with the culture solution, and collect the separated cells for the first digestion, after the first digestion; continue the second digestion, and add the remaining tissue blocks to 10 Ml new trypsin continues to digest. 6. Repeat the 5 digestion step until a small amount of tissue remains. Generally, 4-5 times of digestion can digest most of the tissue pieces (excluding the time when the digestive solution is discarded). 7. The first and second cell-containing digestive juices are placed in a centrifuge tube, passed through a 180 mesh screen, and centrifuged together; the third and fourth cell-containing digestive juices are placed in a centrifuge tube, over 180 After meshing the mesh, centrifuge together. Finally, resuspend the two tubes with 8 ml of 20% serum-containing medium, inoculate them into a 75 cm2 plastic flask, place them in the incubator for 1.5 hours, remove them, and discard the adherent cells (mainly fibroblasts). Cells and endothelial cells were taken out of the unattached cell suspension. After counting by the trypan basket rejection method, the culture solution was added to adjust the cell concentration to 5-6 x 105 cells/ml, and inoculated into the desired culture vessel. 5. Generally, there is no need to add BrdU. If the culture time is long (very few fibroblasts are found), 0.1 mmol/ml BrdU (Sigma) can be added to prevent fibroblast proliferation. With the addition of BrdU, the duration of myocardial cell pulsation will be longer. 9. 24 hours after inoculation, gently rinse the cultured cardiomyocytes with warm medium or balanced salt solution to remove unattached cells (some cells will stick after 24 hours, and many cells overlap and grow). Change the culture solution. Treatment factors can be applied after 48 h or 72 h of incubation as required by the experiment. Third, the results When the cardiomyocytes are inoculated, the shape is round or elliptical, and the wall is almost attached at about 24 h. At this time, the cells protrude from the pseudopod. The pseudopods are fibrous strips under the microscope, and the cell bodies are irregularly shaped, such as Polygon, some cells have a tendency to aggregate, and the cell pulsation effect is better. DMEM medium is dark red in the initial culture, and becomes pale yellow after two days. It should be a manifestation of the decline of nutrients, and also indicates that the cell growth is good. We also supplemented the training methods of some foreign literatures. The easiest way to identify is to beat or not. Note: When the beat is weak, you may not see the beat under a 10x objective, and you may be able to observe it with a 20 or 40x objective. The best way to verify the eligibility of the procedure is to look at the purity and pulsation of the cardiomyocytes. In addition, cardiomyocytes express actin, which can be used as an identification, but not the only characteristic indicator, because smooth muscle cells are also expressed. |
| other | First, the experimental discussion The neonatal rat cardiomyocytes belong to the primary growth cells, and the culture process is cumbersome. There are various concentrations of trypsin digestion methods in the literature, and 0.06% concentration of trypsin has less damage to cells, but this concentration takes longer to digest. Take repeated repeated low-concentration digestion methods. After each digestion, extract the supernatant with a pipette and centrifuge to obtain cardiomyocytes. Using the different adherence time of cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts, the fibroblasts were fully removed by differential adherence for 1.5 h to achieve the purpose of purification. The fibroblast cell body is spindle-shaped or irregularly triangular, with an oval-shaped nucleus in the center, cytoplasmic processes, which are radial when growing, and proliferate, do not beat, and are well differentiated from cardiomyocytes. Digestion and beating must not be excessive, which is the most important principle to ensure the vitality of cardiomyocytes. The seeding density (generally not less than 10 5 /ml) will also affect the pulsation and synchronized pulsation of cardiomyocytes. |
Single Packed Mottled Waxy Corn
Waxy corn comes in a variety of colours. Some people wonder if waxy corn is a genetically modified product. In fact, it is not. Waxy corn originated in China. It is caused by a genetic mutation. Artificial selection gradually led to the emergence of a type of tannin.
Waxy corn, also known as waxy corn, is sticky corn. The grain has coarse, waxy endosperm, similar to shiny, glassy (clear) grains such as hard and dented corn. Its chemical and physical characteristics are controlled by a recessive gene (wx), which is located on chromosome 9. 100% of the starch in the endosperm is straight-chain starch.
Coloured glutinous corn is generally white, yellow, red, purple and black, with white, yellow and purple corn being the basic colours. Purple and white hybrids naturally become purple if the purple gene "beats" the white gene and vice versa, so if the two tie we see white and purple corn. Purple can turn into red and black corn, or as we often say, "red is purple and black is purple". Of these colourful corn, the most common yellow waxy corn is the most nutritious as it is rich in carotenoids...
Currently, the only genetically modified foods sold on the Chinese market are soybean oil and papaya. Waxy maize is a hybrid variety and is not associated with genetic modification. Therefore, it can be concluded that glutinous maize is a hybrid variety and has nothing to do with genetic modification.
Genetic modification is a type of "genetic engineering" in modern science and technology, which makes use of modern molecular biology techniques. Hybridisation is the mating of individuals of different genotypes to produce offspring that are different from the original "pure" breed. In a sense, it belongs to the natural exchange of genes that can occur in nature.
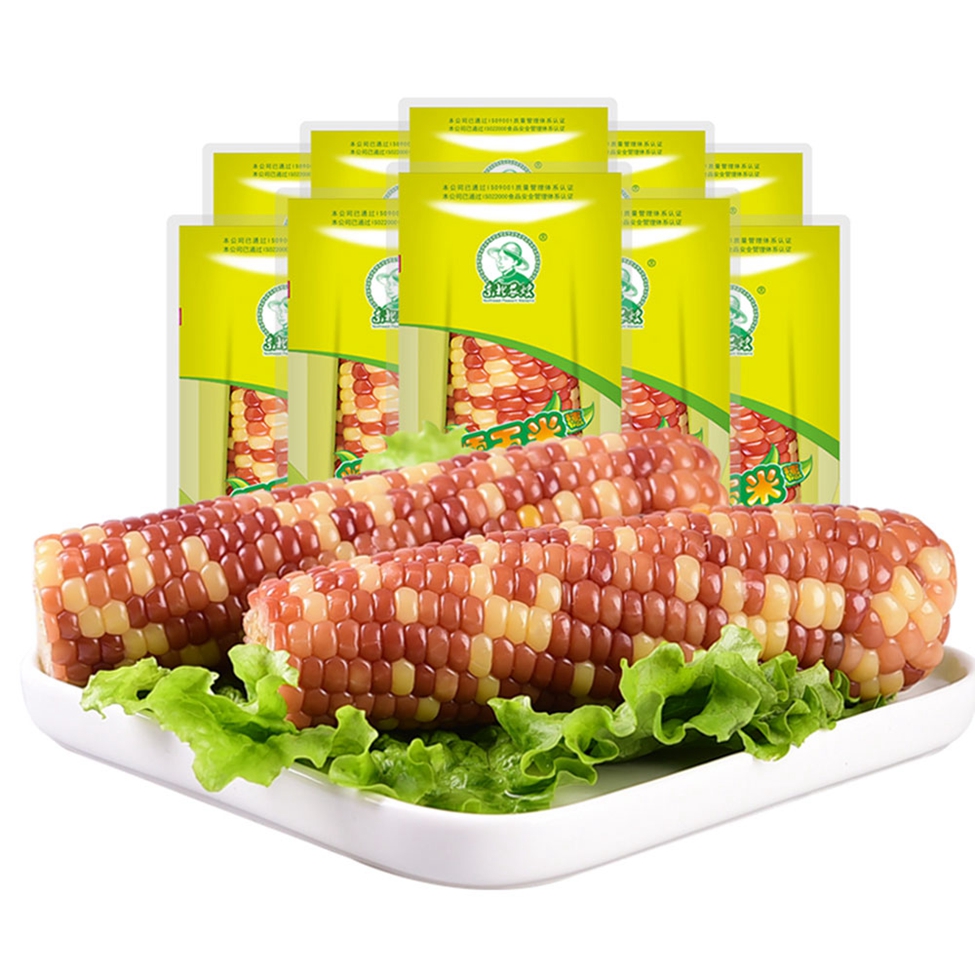
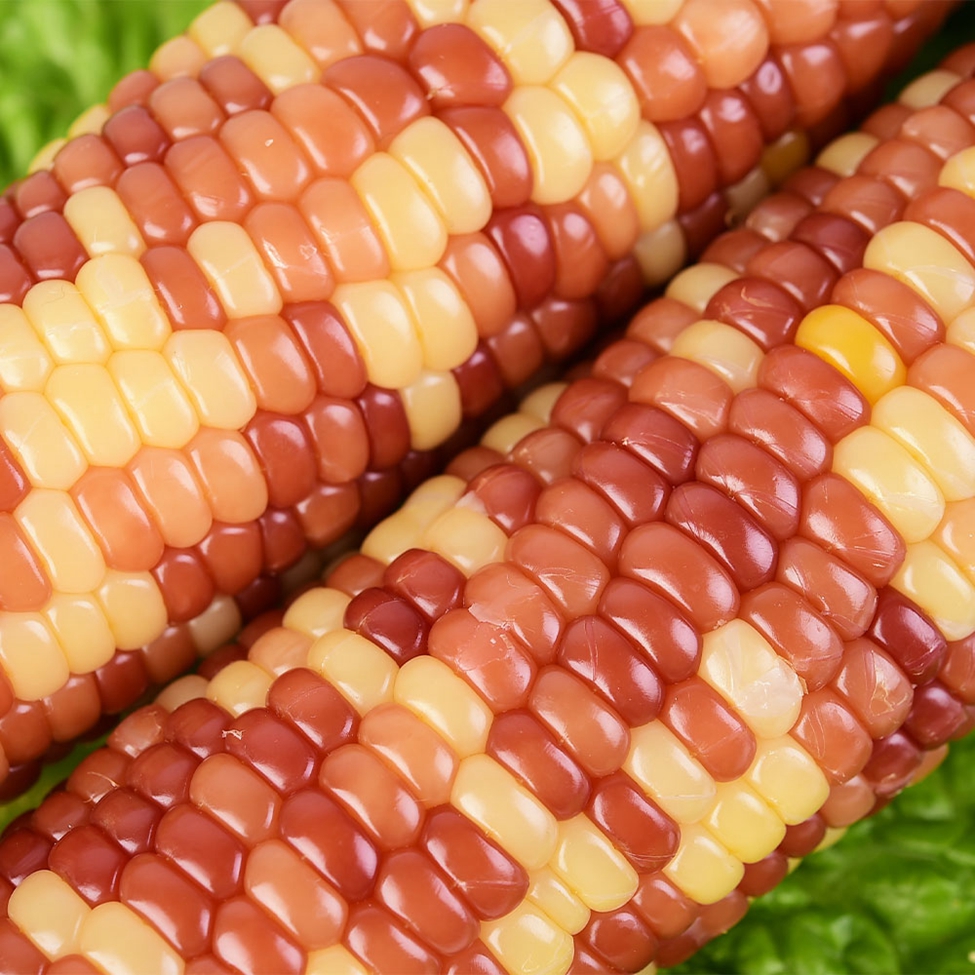


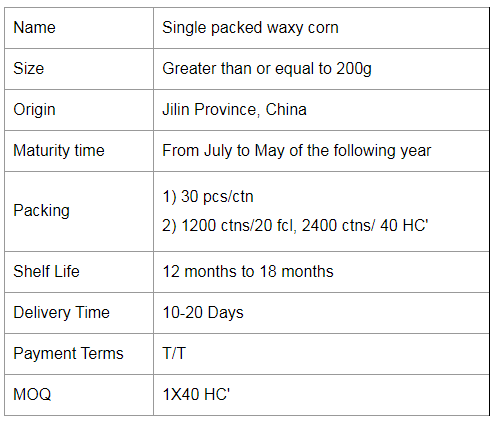
Colorful Waxy Corn,Colorful Mottled Waxy Corn,Single Packed Mottled Waxy Corn,Single Packed Colorful Waxy Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com