RNA extraction and purification considerations
Due to the widespread presence of RNase and the intractable properties that are difficult to inactivate. It makes the extraction and purification of RNA and subsequent work very difficult. | |||
| |||
For RNA purification using the RNeasy Kit, no additional DNase digestion is required, as QIAGEN's patented RNeasy silica membrane technology removes most of the DNA efficiently. However, for some RNA-based sensitive applications, we recommend using the RNase-free DNase Set (see the RNeasy product specification for digestion) to ensure that the resulting RNA is free of any DNA contamination. The main problem with RNA work is to prevent RNase contamination. In addition to the need to pay attention to RNase during operation, what are the points for attention when performing RNA purification for different types of samples? | |||
| |||
Isolation of RNA (such as heart or muscle tissue) from fiber-rich tissues is difficult because the contractile proteins, connective tissue, and collagen in the fibrous tissue interfere with the RNA purification process. Therefore, in order to remove the effects of these proteins, tissue samples require the use of proteases or phenol-containing lysates. At the same time, the above treatment conditions can not cause RNA degradation, QIAGEN recommends using RNase-free proteinase K for digestion. | |||
| |||
Immobilization and entrapment processes can result in severe degradation and chemical modification of nucleic acids, and the nucleic acids we purify from FFPE samples typically have a lower molecular weight than fresh or frozen tissue. The extent of nucleic acid degradation/fragmentation depends on the type of sample and age, and is also strongly dependent on fixation, embedding and storage conditions. Please follow the recommendations below to treat FFPE samples to reduce RNA damage.
| |||
| |||
The red blood cells in the whole blood have no nuclei, the number of practical cells per ml of blood is small, and the nucleic acid yield is relatively low, so the target of separation from whole blood is white blood cells. In addition, contaminants such as the anticoagulant heparin and EDTA and naturally occurring enzyme inhibitors must be removed, all of which interfere with downstream RNA analysis. QIAamp RNA Blood Kits are highly suitable for purifying high quality RNA from human blood samples, eliminating RNases, contaminants and enzyme inhibitors while maximizing genomic DNA contamination. | |||
| |||
RNA, especially miRNA, can be present in serum, plasma, urine, and other body fluids, and is also present in the supernatant of cell culture fluids. The extracellular RNA content is much lower than intracellular RNA, but it is relatively stable and has a half-life of about 2 days in human whole blood. However, repeated freeze-thaw cycles still result in poor purification. Carrier RNA is recommended for purification to improve the efficiency of free RNA recovery. | |||
| |||
Some viruses have single- or double-stranded RNA genomes. Viral RNA is usually isolated from acellular body fluids, and the amount of viral nucleic acids in these samples is very low. Viral particles may need to be concentrated by ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration or precipitation. It is recommended to use carrier RNA during purification to improve the efficiency of recovery of viral RNA. It is also recommended to reverse transcribe certain viral nucleic acids containing complex secondary structures using suitable reverse transcriptases. |
Read the original text: http://
Corn, also known as wheat, maize, grain, it is one of the world's three major food crops, planting area and yield after rice and wheat, ranked third.More because of good mouth, high heat, large yield, and is widely used in a variety of livestock feed, thus known as the "King of Feed", in addition, corn is also the three food crops most suitable for industrial raw material crops, its processing of industrial products as high as more than 3000 kinds.


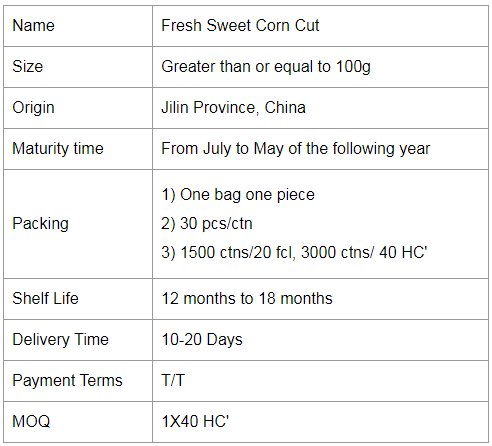
If you have any questions, please leave a comment on this website or contact us using email.
Steam Sweet Corn Cut,Sweet Maize Cut,Fresh Sweet Corn Cut,Baked Sweet Corn Cut
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com